
Dichotomy Examples False Dichotomy (aka False Dilemma, eitheror fallacy / How to use
False dilemma fallacy example in politics. False dilemma fallacy is used in public policy debates when the speaker frames the issue in a way that does not leave room for disagreement with their point of view. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there were heated discussions in the US regarding the best way to handle this unprecedented.

False Dilemma (Logical Fallacy) Definition and Examples
Origin of False Dilemma Fallacy. The history of the 'false dilemma fallacy' term is a bit fuzzy, but thinkers like John Searle and Jacques Derrida have been exploring errors in reasoning for a long time. They and others like them try to figure out how we can communicate and think better by avoiding mistakes like this one.

False Dilemma Fallacy Logic and critical thinking, False dilemma, Logical fallacies
A False Dilemma Fallacy occurs when an argument falsely presents two options or solutions as the only possible choices, ignoring or dismissing the existence of alternative options. Stick around to learn how this fallacy can impact your life, from the political choices you make to the products you buy. We'll explain the term and share some false.

Living on Purpose The false dilemma fallacy Watershed Voice
False dilemma reasoning is an example of slanting by unfairly presenting too few choices. It loads the set of choices unfairly by not offering a fair range of choices. The black-white fallacy is a false dilemma fallacy that limits you unfairly to only two choices, as if you were made to choose between black and white.

What is false dilemma fallacy?
False Dilemma or False Dichotomy is a formal fallacy based on an "either-or" type of argument. Two choices are presented, when more might exist, and the claim is made that one is false and one is true - or one is acceptable and the other is not. Often, there are other alternatives which haven't been considered, or both choices might be.

PPT Fallacies PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1400187
The false dilemma is an informal fallacy, since there is an issue with its premises, and namely with the assumption that both of the following conditions are true, in a situation where one or both of them are false: A false dilemma assumes that the options that are presented are mutually exclusive. In this context, mutual exclusivity means that.
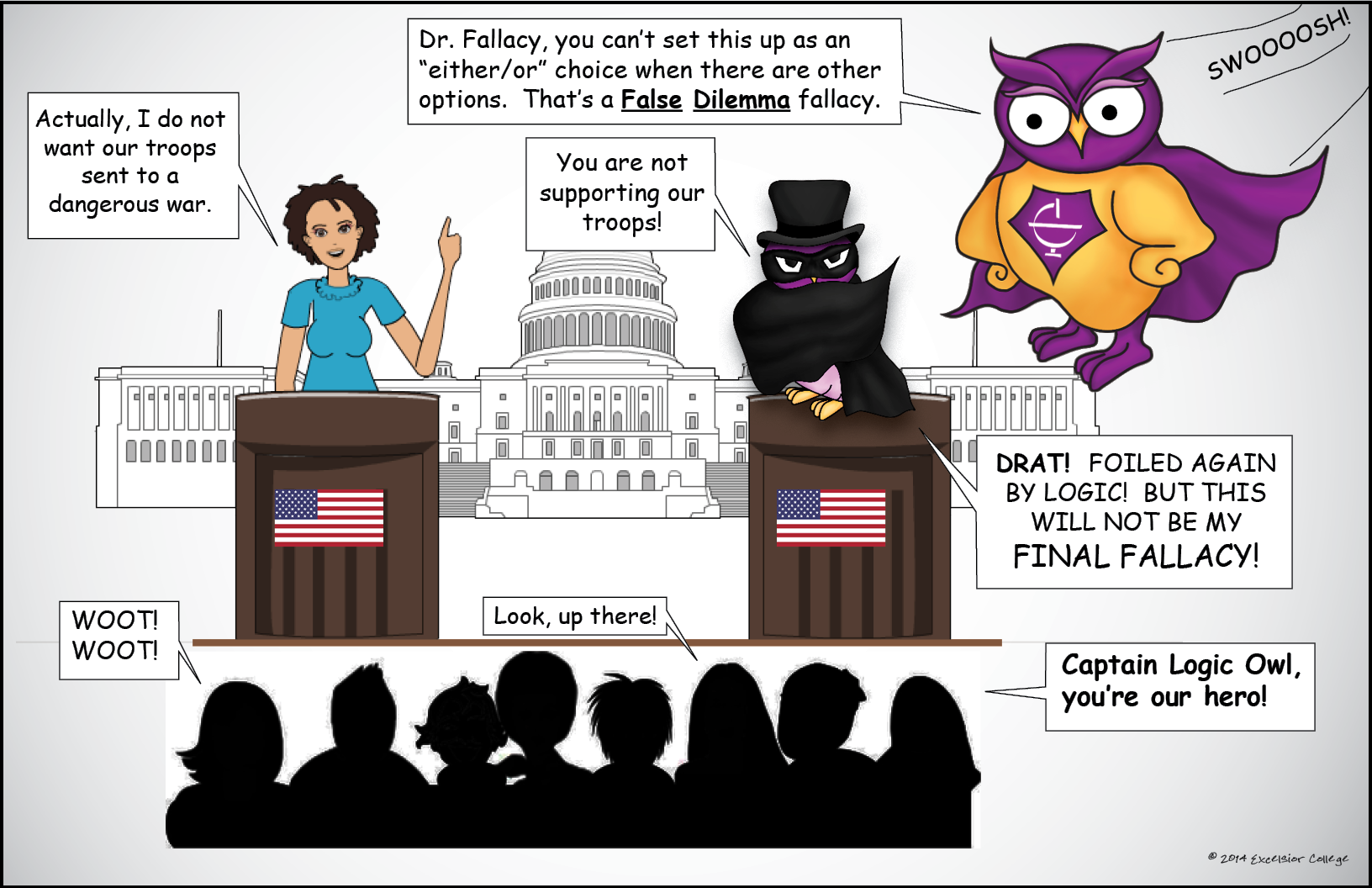
False Dilemma Fallacy Excelsior College OWL
False Dilemma Fallacy. Sometimes called the "either-or" fallacy, a false dilemma is a logical fallacy that presents only two options or sides when there are many options or sides. Essentially, a false dilemma presents a "black and white" kind of thinking when there are actually many shades of gray.

PPT Fallacies PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6695613
The false dilemma fallacy is a logical fallacy that presents two mutually exclusive options or solutions to an issue, disregarding all other possibilities. How does the false dilemma fallacy work? The false dilemma fallacy skews readers' and listeners' understanding of an issue by failing to present its full, nuanced range of options.

PPT What is Argumentation? PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2532748
1. The fallacy of equivocation is an argument which exploits the ambiguity of a term or phrase which has occurred at least twice in an argument, such that on the first occurrence it has one meaning and on the second another meaning. A familiar example is: The end of life is death. Happiness is the end of life.

Logical Fallacies Logical Fallacies are statements that may
False dilemma fallacy is often used as a persuasion technique in advertising to highlight that a specific product or service is the only reasonable choice. In an effort to persuade consumers that their company was the only option for those looking for reputable movers, a United Van Lines TV commercial asked the following questions:.

7 Either Or ("False Dilemma") Fallacy Examples in Real Life Fallacy examples, False dilemma
Similarly, you may have one soda during an evening out as a treat but be well-hydrated from your normal drinking habits and maintain an active lifestyle. There are a lot of options in between the two extremes presented by the speaker in this example. 5. "You're either part of the solution or part of the problem.".
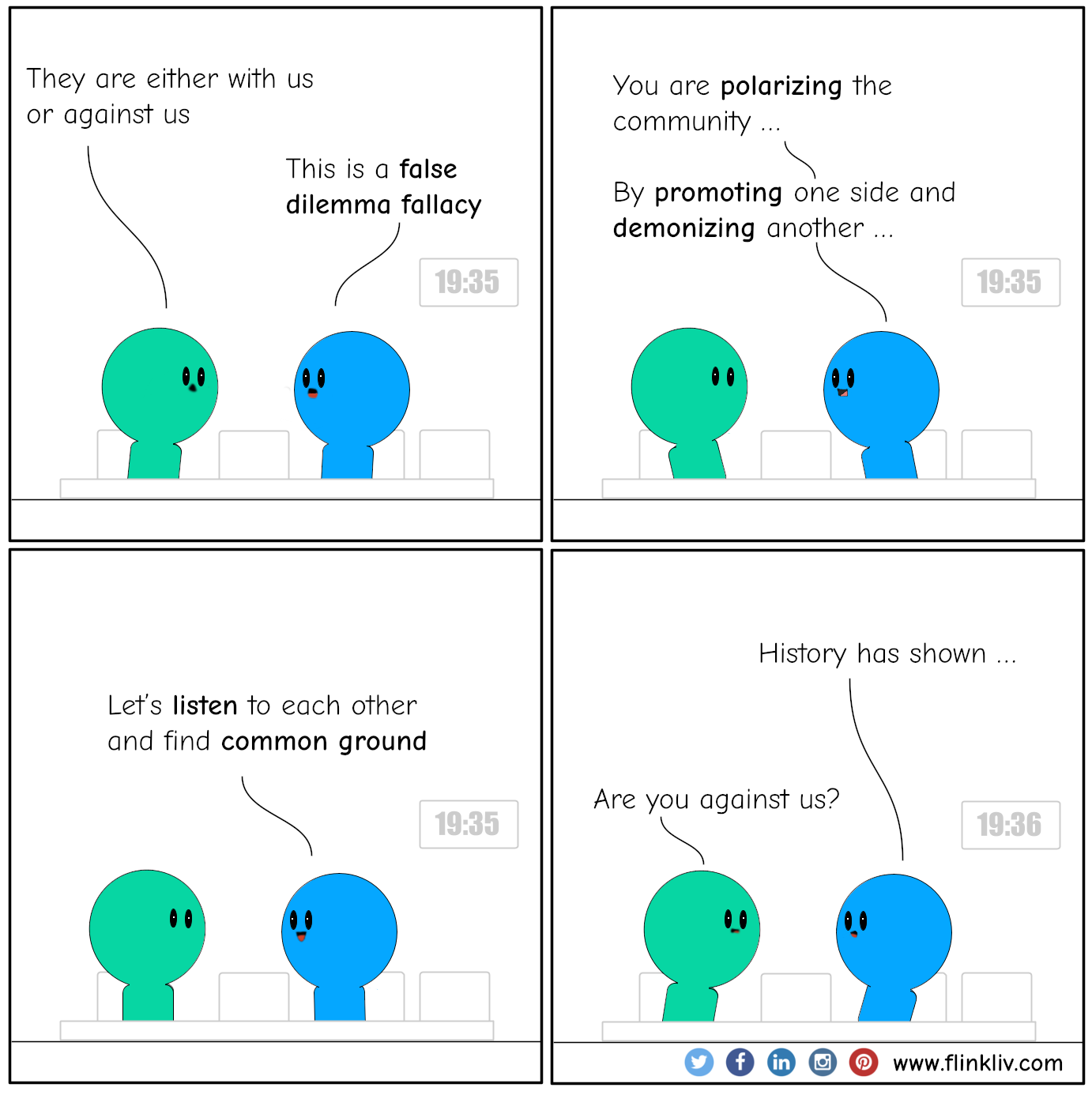
Logical Fallacy Flinkliv
False dilemma. A false dilemma, also referred to as false dichotomy or false binary, is an informal fallacy based on a premise that erroneously limits what options are available. The source of the fallacy lies not in an invalid form of inference but in a false premise. This premise has the form of a disjunctive claim: it asserts that one among.
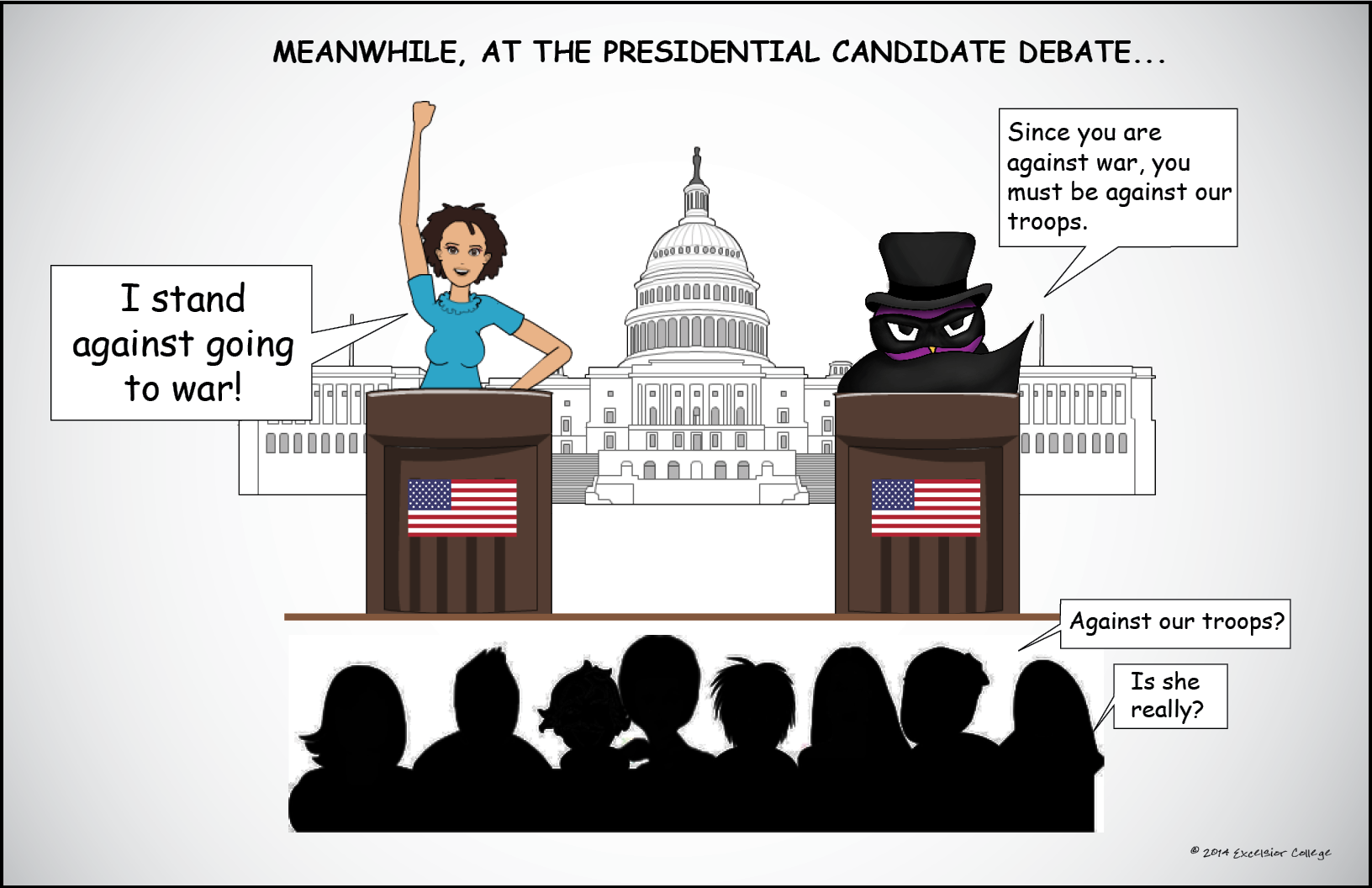
False Dilemma Fallacy Excelsior OWL
A false dilemma is an informal fallacy that falsely presents a situation by proposing only two mutually exclusive options instead of the complete range of options. As per Wikipedia - "a false dilemma is an informal logical fallacy that erroneously limits what options are available."

PPT Critical Thinking Chapter 7 PowerPoint Presentation ID156645
False Dilemma The False Dilemma fallacy occurs when an argument offers a false range of choices and requires that you pick one of them. Usually, the False Dilemma fallacy takes this form: Either A or B is true.. Logical fallacies are errors of reasoning, errors which may be recognized and corrected by critical thinkers. Fallacies may be.

PPT Logical Fallacies PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID326982
Example False Dilemma #1. We can see an example of an argument with misleading or "false" exclusivity below: Coursework is a better predictor of final grades than exams among most school children. As such, we should eliminate exams and focus entirely on coursework. This focuses first on how well coursework and exams predict final grades.

7 Either Or ('False Dilemma') Fallacy Examples in Real Life False dilemma, Fallacy examples
False dilemma fallacy is also known as false dichotomy, false binary, and "either-or" fallacy. It is the fallacy of presenting only two choices, outcomes, or sides to an argument as the only possibilities, when more are available.