PPT Plants and Seeds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID791432
Seed Anatomy Seeing Seeds Close-up - These pictures are of a pea seed Here you can see, I've removed the seed coat and split the seed in half. One half has the embryo and some of the stored food, and the other half holds the rest of the stored food. This picture is of the half of the seed that has the embryo. This picture is a close-up of the embryo.

Seed anatomy of a dicotyledon. Download Scientific Diagram
What are the Different Parts of a Plant Broadly, plants have two organ systems: A) the root system and B) the shoot system. A typical diagram of a plant body consists of three parts: 1) roots, 2) stems, and 3) leaves, each having specialized functions. Apart from these basic parts, a flowering plant also contains 4) flowers and 5) fruits.

Seed Parts and Sprouting Starts The Edible Schoolyard Project
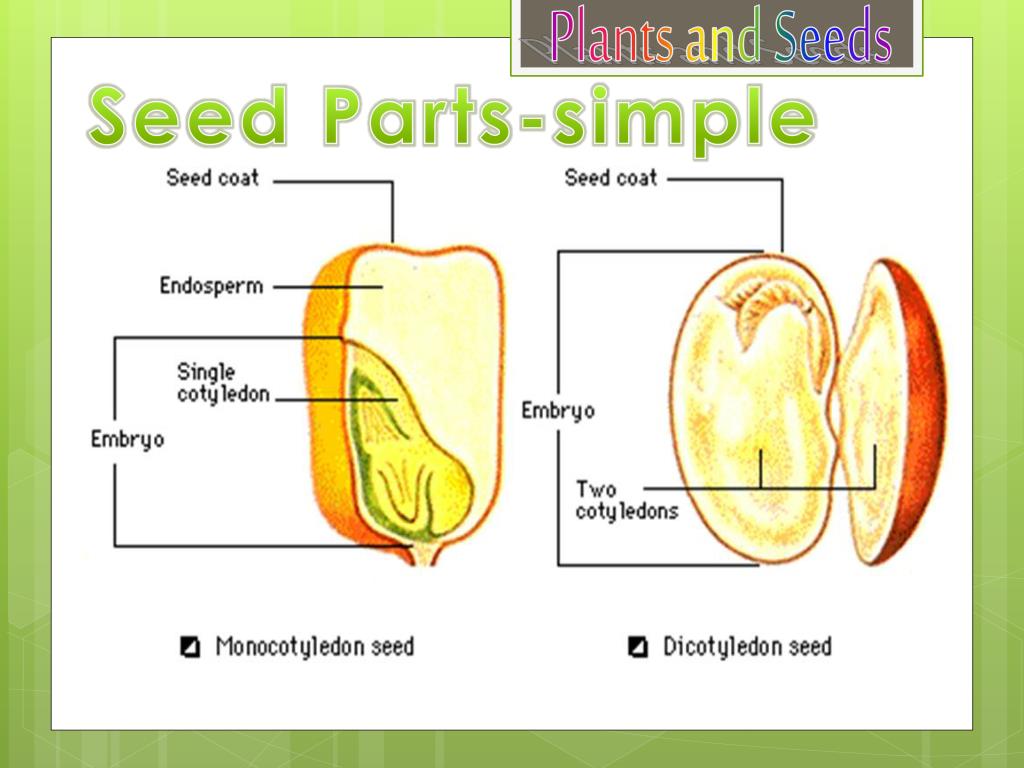
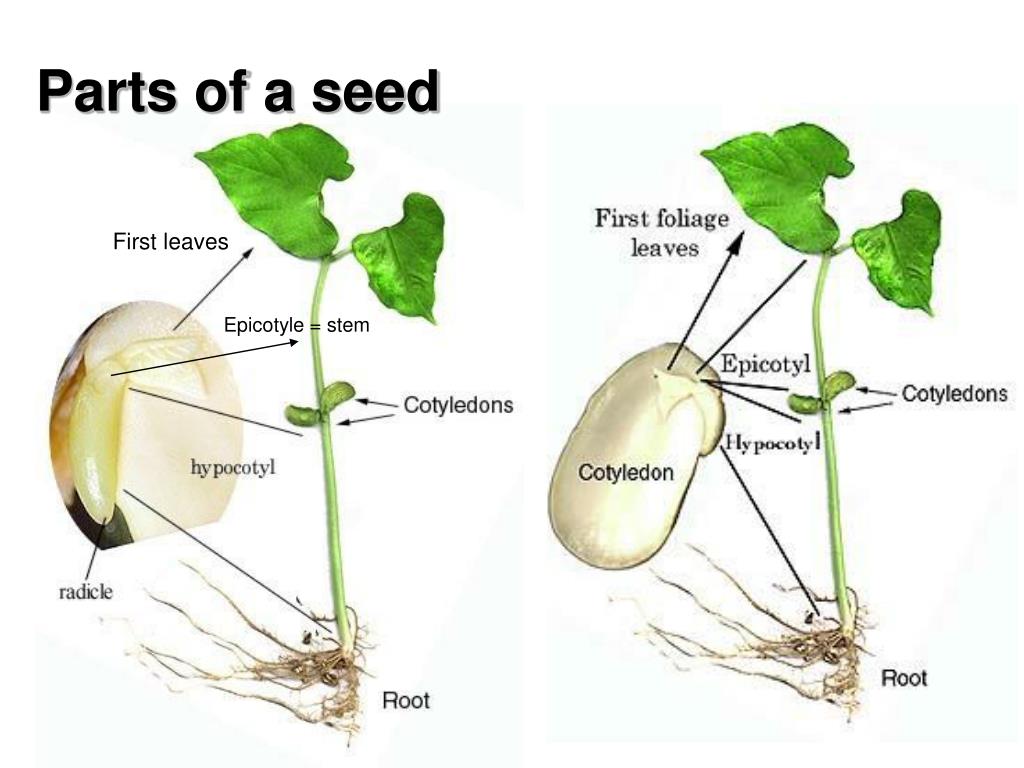
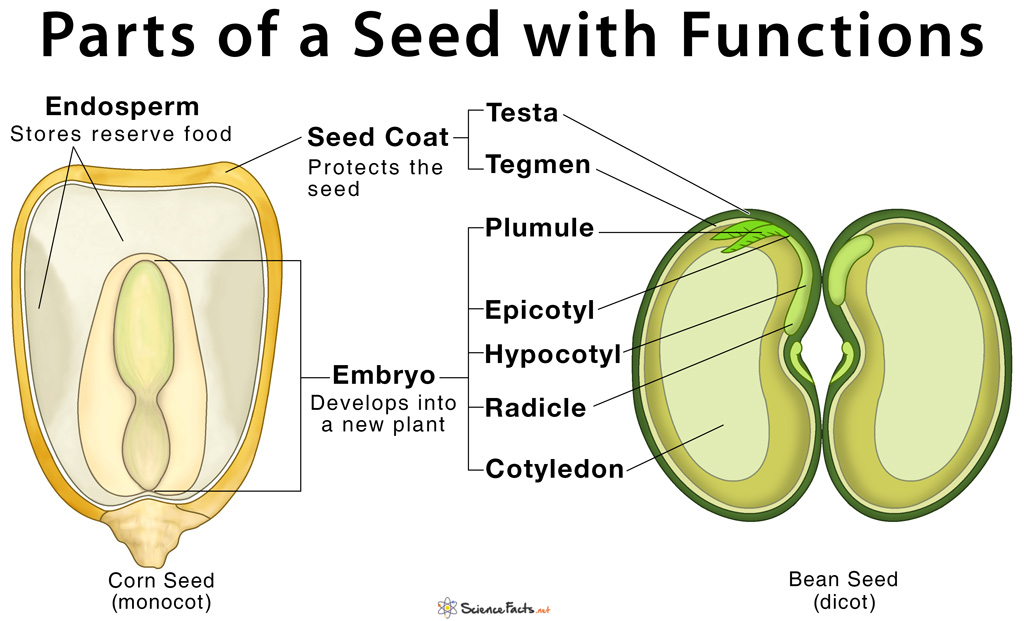
It consists of three parts: a plumule that forms the shoot, a hypocotyl that forms the stem, and a radicle that forms the root. Structures of dicot and monocot seeds - LibreTexts (CC BY-NC-SA) The seed coat consists of one (in monocots) or more (in dicots) protective layers that encase the seed. In dicots, the seed coat is divided into an.
Plant the Seed
Learn about the parts of a seed and draw your own diagram.

Seed Definition, Types, Structure, Development, Dispersal, Uses
This article provides a diagram of the various parts of a seed, including the seed coat, embryo, endosperm, and cotyledons. Learn about the function and structure of each part and how they contribute to the growth and development of a plant from a seed. Skip to content Circuitry Blueprint Depot Browse Our Electronic Schematic Designs

Seed Plant Seed Definition, Parts, Types, Structure, Functions
Seeds and diversity. To review, the two fundamental ways of propagating plants and how they differ in their outcomes are s exual reproduction through seeds or spores, and a sexual or vegetative reproduction through manipulation of various plant parts, including cuttings from leaves, roots, and stems, or grafting.. Asexual reproduction, also called vegetative propagation, normally results in.
PPT Seeds and Growing Plants PowerPoint Presentation ID229013
A typical seed consists of the following parts: Source: Google Tesla: It is the outer coat of the seed that protects the embryonic plant. Micropyle: It is a tiny pore in the testa that lies on the opposite of the tip of the radicle. It permits water to enter the embryo before active germination.

Anatomy Of A Bean Seed Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
Quiz Course 29K views How a Seed Becomes a Seed All seeds need to have directions to know what to become and what to look like. These directions come from two different parts of a plant:.

Parts of a Seed Imago
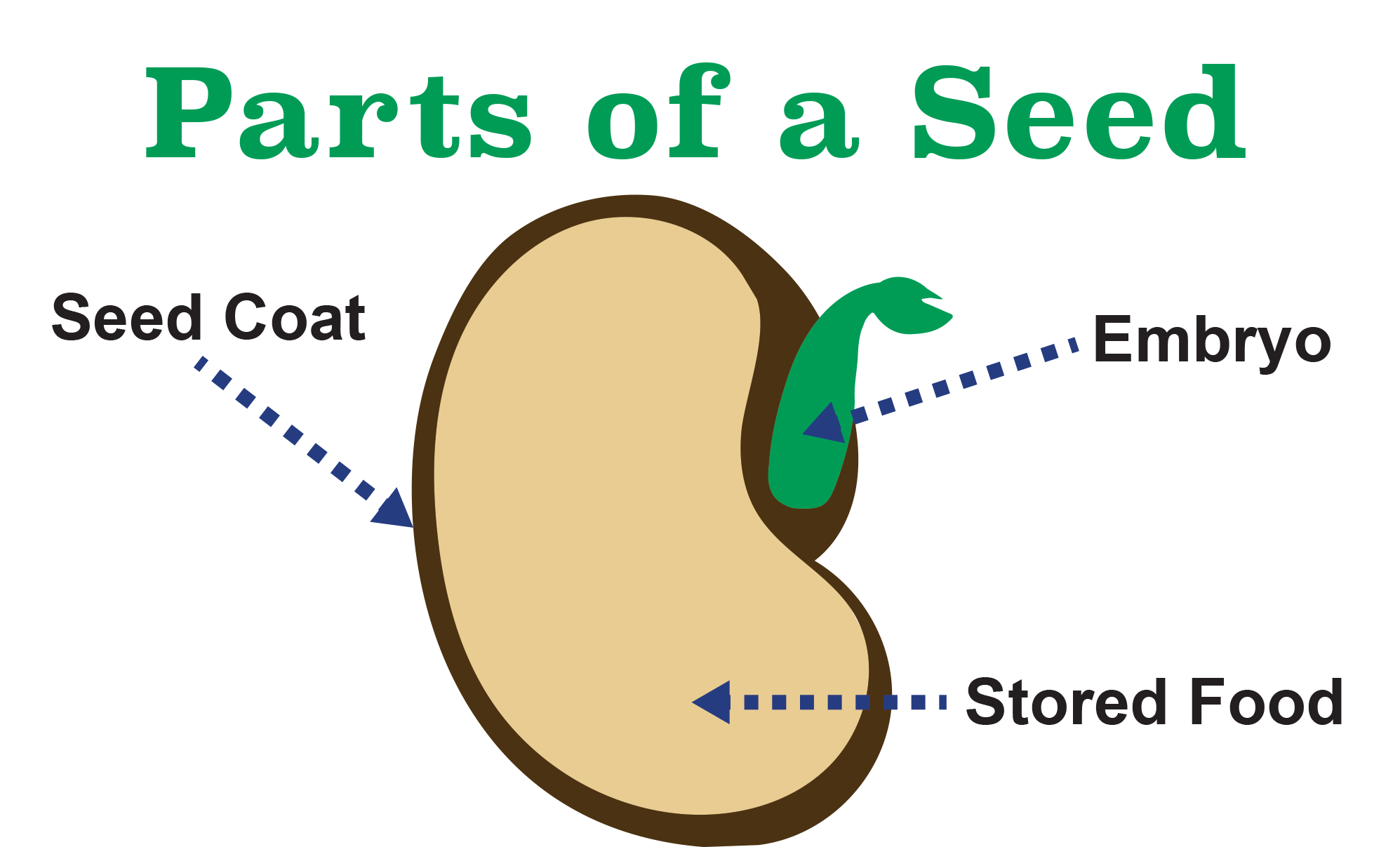
The place where food is STORED for a young plant. Also called ENDOSPERM. germinate. The process when a plant begins to GROW from a seed. seedling. a YOUNG plant. radicle. The part of the embryo that grows into the ROOT of the plant. Plumule.

Seed anatomy of a dicotyledon. Download Scientific Diagram
Seed Growth. In angiosperms, the process of seed development begins with double fertilization and involves the fusion of the egg and sperm nuclei into a zygote. The second part of this process is the fusion of the polar nuclei with a second sperm cell nucleus, thus forming a primary endosperm. Right after fertilization, the zygote is mostly.

seed germination Google Search Plant science, Teaching biology, Teaching science
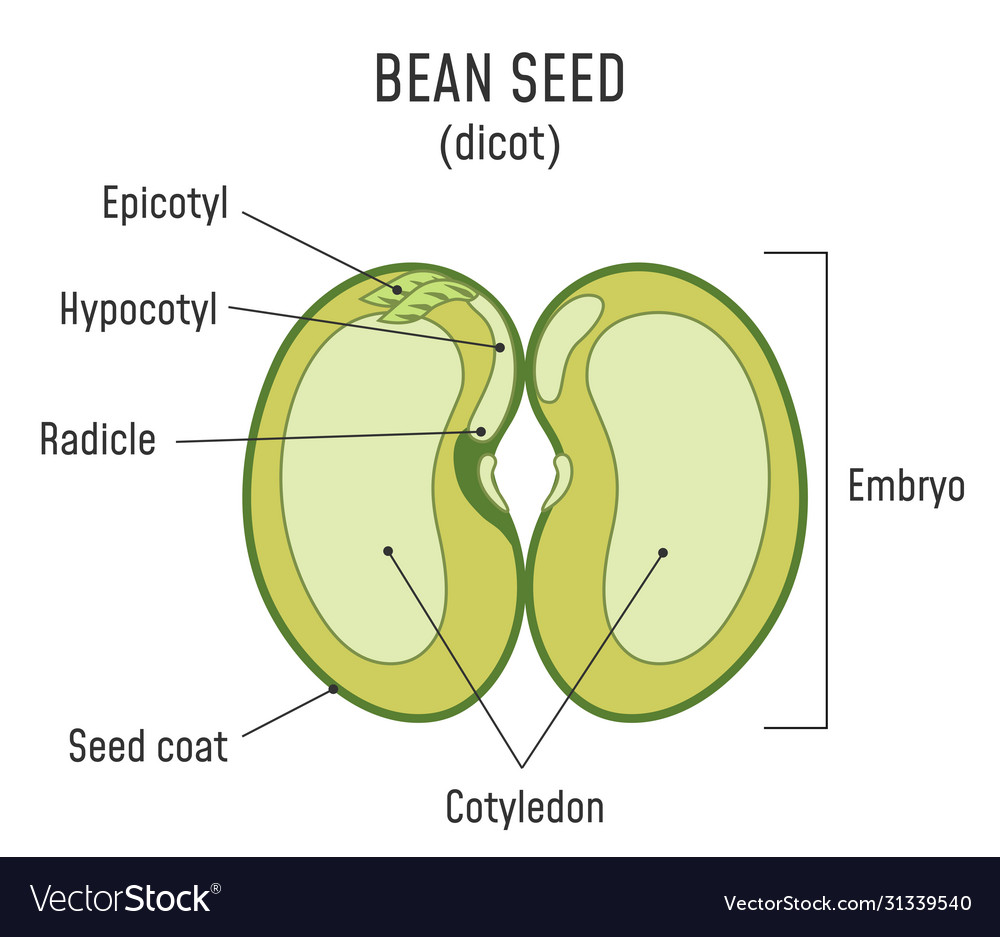
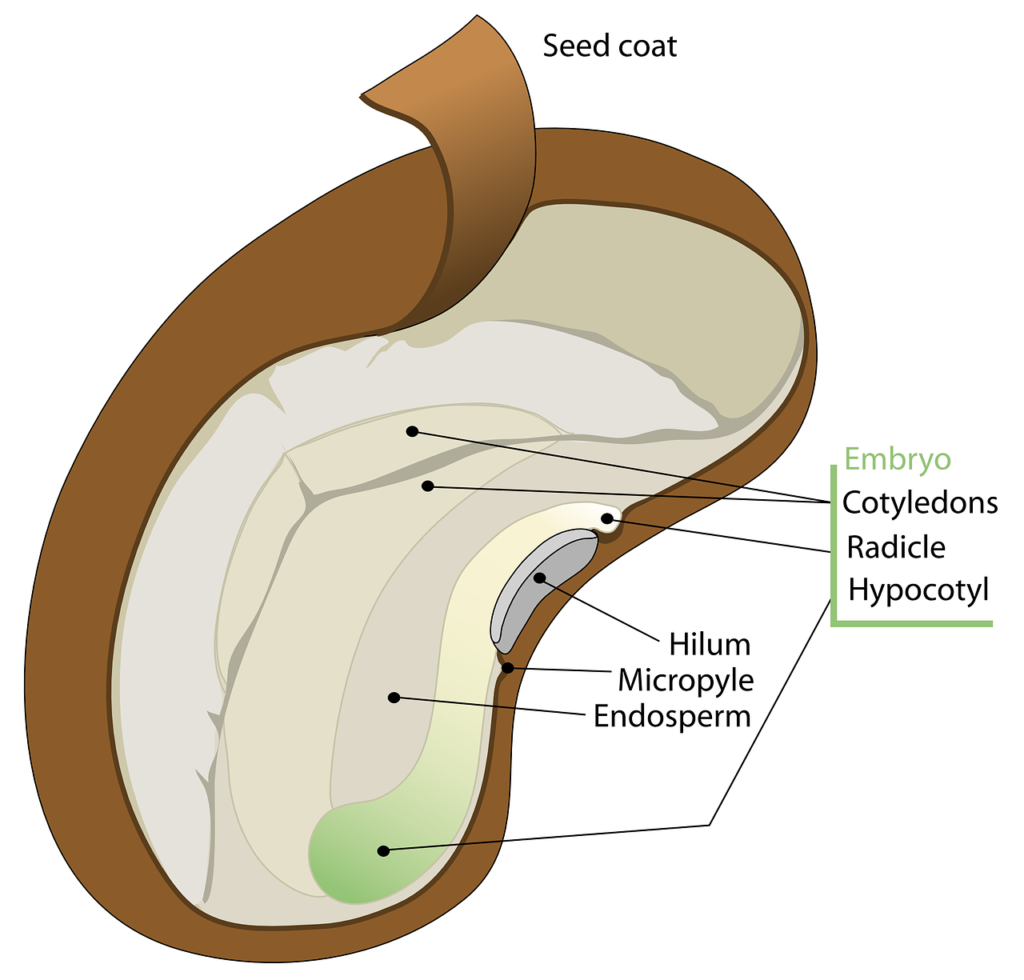
Figure 4.6.3.1 4.6.3. 1: The external structures of a bean seed, an example of a eudicot (7X). The seed coat surrounds the seed. There is a round micropyle, where the pollen tube originally entered the ovule. The oval hilum is a scar from where the ovule was attached to the ovary. Image by Melissa Ha ( CC-BY ).
Bean seed structure anatomy grain dicot seed Vector Image
There are three basic parts of a seed in the angiosperms: (a) an embryo, (b) food storage or nutritive tissue, and (c) seed covering. Embryo A mature seed has a diploid (2N) embryo which develops from a fertilized egg or zygote. It results from the union of a sperm (1N), from a germinated pollen, with a female egg (1N) in the embryo sac.
5 Seed Facts Amazing Reproductive Strategy Jake's Nature Blog
A seed has three parts: Seed Coat Endosperm Embryo Seed Coat A seed coat protects the internal parts of a seed. The seed coat has two layers. The outer layer is thick and known as the testa. The inner layer is thin and known as tegmen. A thick seed coat protects the seed from sunlight and water.
Blog Feed Wildlife and Ecology
Definition of Seed: A true seed is defined as a fertilized mature ovule that possesses embryonic plant, stored material, and a protective coat or coats. Seed is the reproductive structure characteristic of all phanerogams. The structure of seeds may be studied in such common types of pea, gram, bean almond or sunflower.

Diagram showing parts dicot seed on white Vector Image
Diagram of seed | Parts Of A Seed Drawing | How To Draw Parts Of A Seed | Bean Seed (Dicot) DiagramSubscribe for More videos: https://www.youtube.com/user/k.
.PNG)
Reproduction in Flowering Plants Presentation Biology
published February 20, 2023 Sometimes in life, we take things for granted. For most gardeners, what's inside of a seed is one of those things. We poke them into the ground or seed-starting medium and wait (sometimes impatiently) for the seeds to sprout. Yet, fully understanding the process of germination begins with the anatomy of the seed.